No products in the cart.
Women's Talk
Breast Cyst: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment And Prevention
Breast Cysts are noncancerous (benign), fluid-filled sacs or lumps, inside the breast. It is common to have more than one cyst in a breast, which gives an appearance of a grape bunch and a water balloon.
It is estimated that 7% of women may develop breast cysts in the western world. Treatment is not always needed. If the cyst is quite large and uncomfortable, then the fluid from the cyst can be drained off, using a needle.
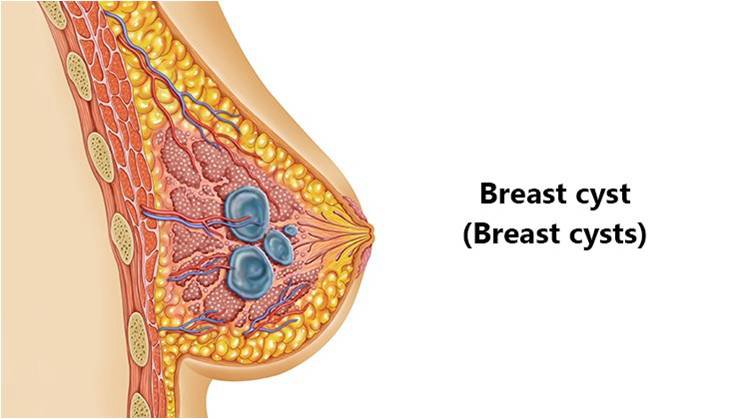
What is a Breast Cyst?
Breast cyst or cysts are the fluid accumulated sacs in the breast, resulting in round or oval breast lumps (nodules). It is common to have multiple cysts, in one or both of the breasts. Cyst development is common in premenopausal women, aged between 35 to 55. Breast cysts will disappear after menopause, but the women using hormone therapy can develop cysts, after menopause also. Mostly, these cysts are benign, but in some people, having the family history of cancer, cysts can be the cause of underlying disease condition.
Causes of Breast Cysts:
The exact causes for breast cysts are unknown till now. Some of the possible causes are:
Breast cysts may develop due to hormonal changes during menstruation in the body. Evidence suggests that high production of estrogen in the body can cause breast cysts, by stimulating the breast tissue.
Cysts are usually, seen on the lobules that produce milk, and carries it to ducts, known as terminal duct lobular unit (TDLU). The possible cause of cyst is due to swelling or inflammation near TDLU.
Sometimes, infections tend to be a possible cause of cyst along with redness, pain and discharge. It is slightly commonly in pregnant and breastfeeding women.
Symptoms of Breast Cysts:
Some of the signs and symptoms of breast cysts are as follows:
- Easily movable, smooth breast lumps with distinct edges
- Breast pain and tenderness (pain or discomfort) near the lump
- Nipple leakage or discharge that may be clear and straw colour
- Increase in lump size just before menses
- The decrease in lump size and the onset of other signs and symptoms after menses
Usually, a breast cyst doesn’t increase the breast cancer risk. Cysts may be responsible for creating difficulty in examining the other lumps in the breast that needs the doctor’s evaluation.
How to Diagnose a Breast Cyst?
Once the lump or cyst in a breast is detected, the doctor will inquire about patient’s medical history. Breast examination is performed by the doctor, and may order mammogram and breast ultrasound for accurate diagnosis. The methods of diagnosis include:
Breast Exam: Physical examination of a breast will be conducted to check for lumps and other abnormalities. Further tests, such as fine needle aspiration and imaging technique can confirm the presence of cyst and lumps.
Breast Ultrasound: This test helps the doctor in knowing, whether the lump is solid or soft liquid filled sac. Mostly, solid lumps are noncancerous, but some can be due to an underlying disease like cancer. The biopsy is recommended, for further evaluation of solid tumours.
Fine-needle Aspiration: It is a method, of insertion of a fine-needle into the breast lump, to withdraw or drain the fluid from the cyst. Ultrasound is used during this procedure to guide the placement of needle in the breast lump. If the fluid, leaks out from the breast lump, immediate diagnosis is needed.
- If the fluid is clear and the breast lump disappears: No further treatment is required.
- Bloody fluid with the appearance of breast lump: Samples are collected, and send to labs for further diagnosis and testing. Surgeons and radiologist will carry out imaging procedures, for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
- No fluid: The doctor will recommend an imaging test, such as mammogram and ultrasound to know if the lump is solid or semisolid. The solid or semisolid lump is collected and observed for cancer.
What is the Treatment for Breast Cyst?
No treatment is required, for the breast cyst filled with fluid, and not showing any signs and symptoms. If the lumps are present and persist for a longer time, then the treatment is needed.
Fine-needle Aspiration: In this procedure, fluid from the breast lumps is drained off, using a fine-needle. The disappearance of a cyst and the resolved symptoms are observed. In some people, formations of recurrent cysts are common. If the lumps persist in the body and grow in size, after 3 to 4 cycles of menstruation, then the doctor’s evaluation is needed.
Hormone Therapy: Oral contraceptives (birth control pills) can regulate normal menstrual cycle and reduce the recurrence and new cyst formation in the breast. If the symptoms are severe, then oral medications, like tamoxifen and danazol are prescribed. On discontinuation, of hormone therapy after menopause, breast cysts can be reduced and prevented.
Surgery: It is surgical removal of breast cysts, usually performed in rare cases, such as recurrence of cyst every month and bloody fluid or tinge of blood in cyst fluid.
What are the methods of Prevention of Breast Cyst?
Breast cyst development can be prevented, by following some measures:
- Wearing a well-fitted supportive bra: It gives relief from discomfort due to painful cysts.
- Applying Hot and Cool Compressors: It helps to reduce pain in the breast.
- Avoiding Caffeine: No such evidence, are present that shows caffeine as a risk factor for breast cysts. However, some women with breast cysts have suggested that avoiding caffeine, can improve the symptoms of breast cysts.
- Reducing Salt Intake: According to some studies, less sodium intake can reduce excess fluid retention in the body, thereby prevents the breast cyst formation.
- Taking over-the-counter medication (acetaminophen and anti-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs), for breast cysts can reduce the pain.
- Exercising regularly, avoiding stress and maintaining a good diet can prevent the breast cyst development.
BY MEDFIFE.COM